Selected Software
This page contains selected Open Source software projects created by the Knowledge Technology Group.
|
|
|
Source code of Ball Localization CNN - Paper (RoboCup, 2016)
D. Speck, P. Barros, C. Weber, S. Wermter (2016) Ball Localization for Robocup Soccer using Convolutional Neural Networks. RoboCup 2016: Robot World Cup XX. |
|
Source Code
https://github.com/Daniel451/BachelorThesisContact:
Pablo Barros, Cornelius Weber, Stefan Wermter|
|
|
Domain- and Cloud-based Knowledge for Speech Recognition - DOCKS
Source Code
https://github.com/knowledgetechnologyuhh/docksContact:
Johannes Twiefel, MSc, Dipl.-Inform. Stefan Heinrich,Professor Dr. Stefan Wermter, Dr. Timo Baumann Dipl.-Ing. Erik Strahl
|
|
|
 This is the source code (Python) for the paper "Ball Localization for Robocup Soccer using Convolutional Neural Networks", which proposes a new approach for localizing the ball in RoboCup humanoid soccer. A deep neural architecture is used without any preprocessing at all. The localization part gets solved by a convolutional neural network that is trained with probability distributions on full images. No sliding-window approach is used. The paper was written in the context of the Bachelor Thesis of Daniel Speck. The paper won the Best Paper Award for Engineering Contribution at the 20th Annual RoboCup International Symposium 2016 in Leipzig, Germany.
This is the source code (Python) for the paper "Ball Localization for Robocup Soccer using Convolutional Neural Networks", which proposes a new approach for localizing the ball in RoboCup humanoid soccer. A deep neural architecture is used without any preprocessing at all. The localization part gets solved by a convolutional neural network that is trained with probability distributions on full images. No sliding-window approach is used. The paper was written in the context of the Bachelor Thesis of Daniel Speck. The paper won the Best Paper Award for Engineering Contribution at the 20th Annual RoboCup International Symposium 2016 in Leipzig, Germany.
 Google, Apple, Bing, and similar services offer very good and easily retrievable cloud-based automated speech recognition (ASR) for many languages and are taking advantage of constant improvements on the server side. However, these ASR systems cannot be adapted with domain knowledge (e.g. by restricting the recognizer to a fixed vocabulary, grammar, or statistical language model) which may result in poor application performance.
Google, Apple, Bing, and similar services offer very good and easily retrievable cloud-based automated speech recognition (ASR) for many languages and are taking advantage of constant improvements on the server side. However, these ASR systems cannot be adapted with domain knowledge (e.g. by restricting the recognizer to a fixed vocabulary, grammar, or statistical language model) which may result in poor application performance.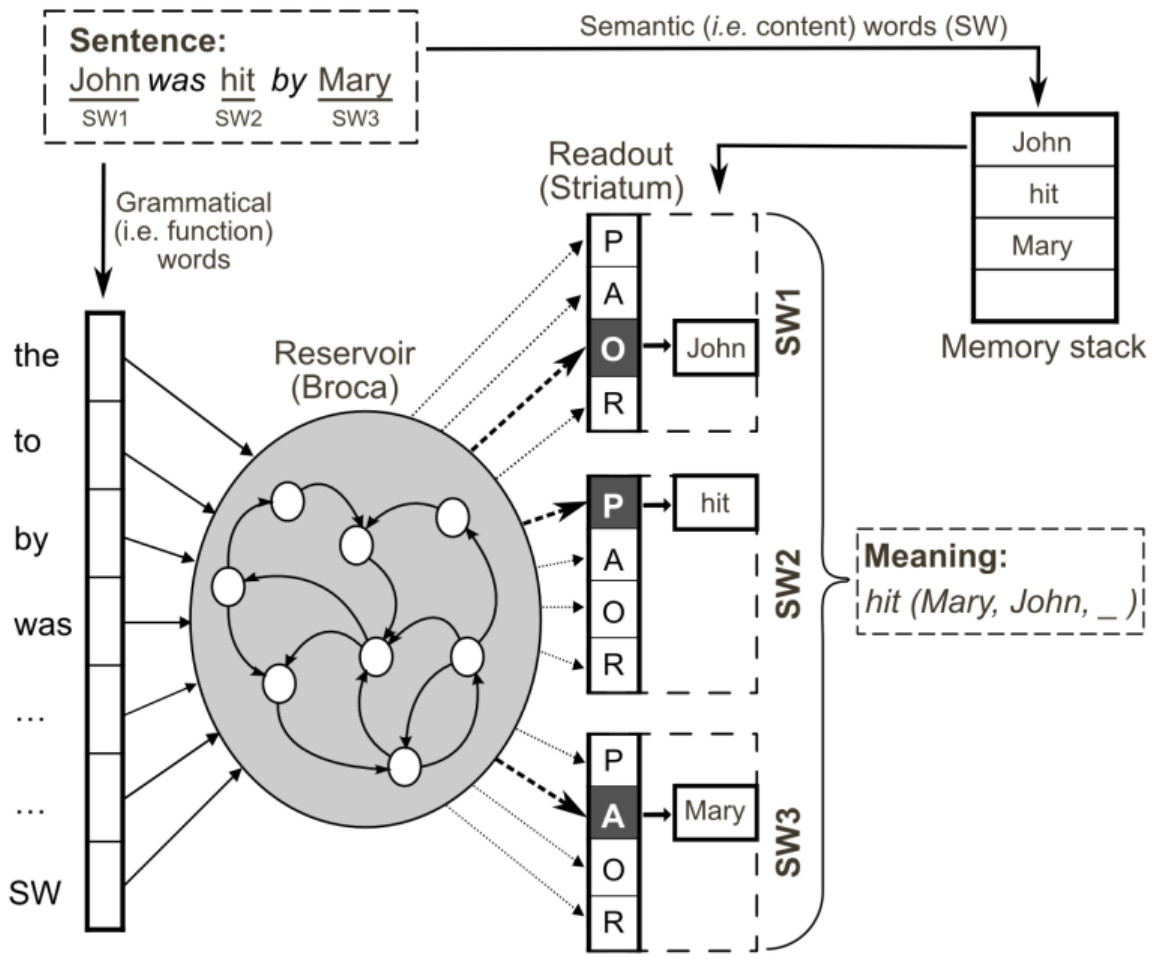 This is the source code (Python) given in supplementary material of our
PLoS ONE paper of 2013. It enables to reproduce experiments of the paper
and gives a full access to the model: you will be able to modify all the
parameters and change the model. It uses Python libraries like Numpy,
and also uses the Oger toolbox developed within the EU FP7 Organic
(2009-2013) project.
This is the source code (Python) given in supplementary material of our
PLoS ONE paper of 2013. It enables to reproduce experiments of the paper
and gives a full access to the model: you will be able to modify all the
parameters and change the model. It uses Python libraries like Numpy,
and also uses the Oger toolbox developed within the EU FP7 Organic
(2009-2013) project.